What is the relationship between genetics and type 2 diabetes? How can one avoid developing the disease? Genetics are not the only factor in type 2 diabetes.
While the main cause is insulin resistance brought on by genetics and lifestyle choices, other factors, such as obesity, physical inactivity, high blood pressure, depression, and gestational diabetes, can also contribute to the disease.
Listed below are some risk factors for type 2 diabetes and ways to reduce them. Read on to learn more! You may be surprised to learn that type 2 diabetes is largely preventable.
Can genetics cause diabetes?
Although environmental factors may play a role in the development of Type 2 diabetes, genetics can be a significant contributor. Genetic research has progressed significantly in the 1980s, and loci explaining the hereditary components of the disease were identified.
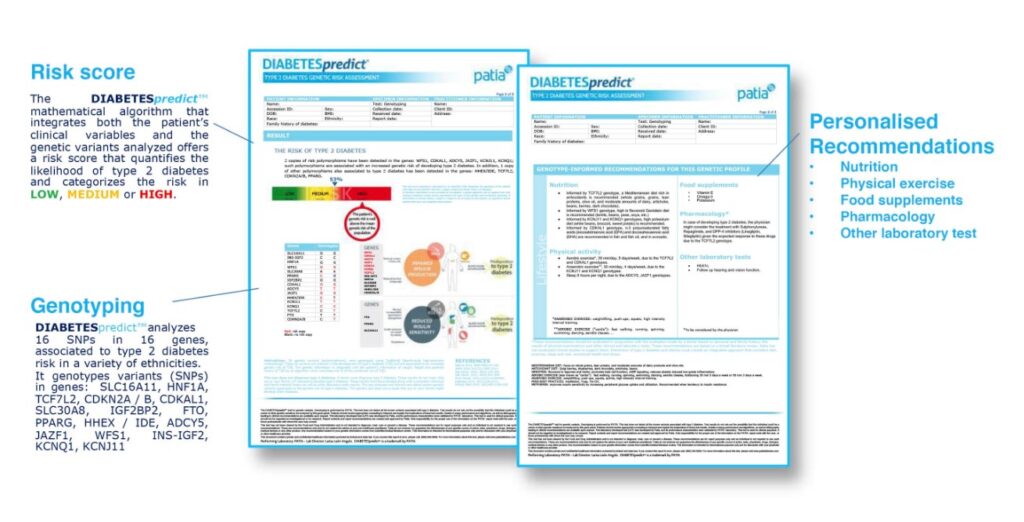
Genetic studies also indicate that some types of diet are associated with higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes than others. These studies provide important information for personalized care. In addition to studying genetics, researchers also have uncovered environmental factors that increase the risk of developing the disease. Diet and exercise are two great ways to prevent and control diabetes.
Diet factors
Several prospective cohort studies have demonstrated an association between diet and type 2 diabetes. Western diets have been associated with elevated blood glucose, inflammatory biomarkers, and oxidative stress, which can damage cell DNA and cause inflammation. In addition,
Western diets have also been associated with increased BMI, elevated lipid levels, and poor glycemic control. Nonetheless, the exact relationship between diet and type 2 diabetes is unclear.
When planning a diet, you should include a variety of fruits and vegetables and a source of unsaturated fat. Most physicians recommend a low-fat diet that includes a combination of vegetables and nuts. You should also include at least two portions of oily fish a week, as these are great sources of Omega-3. In addition, you should avoid saturated and trans fats, and consume fewer sugars and salts.
Exercise
Among people with type 2 diabetes, exercise is a key component in lowering blood glucose levels. Daily activitiy can also greatly reduce the chances of developing diabetics high blood sugar.
The recommended amount of exercise is five to ten hours of moderate-intensity aerobic activity. This may include walking, jogging, swimming, or playing sports like basketball or tennis.
In a typical week, this amount of exercise can be attained by walking for 150 minutes at four miles per hour or jogging for 75 minutes at six miles per hour.
However, most people with type 2 diabetes do not have the aerobic capacity for such intense exercise and may have orthopedic limitations. Don't overstress your body if you cannot reach these exercise landmarks.
The impact of exercise on insulin action is transient, and the effects are short-lived. Therefore, it is important to exercise daily or at least every other day.
Although the acute effects of aerobic exercise last only a few hours, over a 48-hour period, the glycemic response to the same amount of exercise is comparable. Although this isn't conclusive, it is still an important factor to remember for anyone with type 2 diabetes.
Risk factors
Research has shown that the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes increases with genetic risk factors, as measured by body mass index or BMI and disposition index. With increasing risk alleles, BMI, and disposition index, people are more likely to develop diabetes.
These results were consistent across studies of approximately 200 million people. However, they have not proven that the genetic risk factors are the sole cause of the disease. Healthy lifestyle choices are still the most effective prevention strategies.
Botton line
Researchers have identified numerous genetic mutations that are associated with type 2 diabetes risk. While each gene makes only a small contribution, every additional mutation increases the risk. People with type 2 diabetes are at risk for developing the disease at an accelerated rate.
That being said, lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, are important in lowering the risk of insulin resistance and developing type 2 diabetes.
See our reviews of the best blood sugar supplements for alternatives to help you cope with pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes.